Key Applications of Infrared Transmitting Polycarbonate
Gain a comprehensive understanding of the applications of infrared-transmitting polycarbonate in various fields and industries.
The global infrared emitter and receiver market has increased by $677 million, with a CAGR of 4.9% in 2023. These statistics indicate that the use of IR-based technological solutions will increase significantly in the upcoming years.
Experts are already using IR by integrating it with various types of materials in equipment and tools for different industries like defense and military, healthcare, construction, restaurants, etc. Among these, a considerable amount of use of IR-passing materials that block visible and UV rays can be observed.
The same goes for the infrared-transmitting polycarbonate. Considering its growing use, we would like to inform the various industries’ professionals, product designers, manufacturers, etc., about its most common but important applications.
Understanding of IR Transmitting Polycarbonate
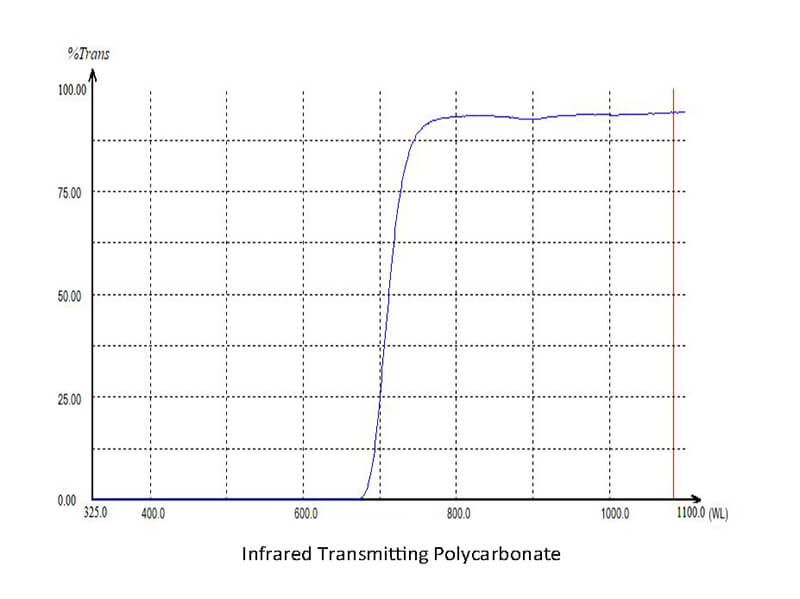
Infrared-transmitting polycarbonate is also known as IR polycarbonate to professionals and manufacturers. By definition, IR passing polycarbonate blocks visible and UV lights due to the implemented specialized pigments or/and coating of 700 nanometers to 2500 nanometers wavelengths.
During the blocking of the visible and UV rays, IR polycarbonate allows the passing of the below-listed infrared radiations.
Working Process of IR Transmitting Polycarbonate
In the working process, the wavelengths of the used pigments or coatings block the visible light as their wavelength ranges from 400 to 700 nanometers, which is lower than the wavelength of the implemented pigment or coating on the polycarbonate sheet or product.
As a result, visible light cannot pass through the polycarbonate. Again, the UV wavelengths range from 100 to 400 nanometers and are blocked by the respective IR polycarbonate sheet or product.
Characteristics of Infrared Transmitting Polycarbonate
Apart from the IR passing and visible light blocking, there are several key characteristics associated with it.
Production Process of IR Polycarbonate
First, polymerization of bisphenol A and carbonyl dichloride (COCl2) happens within the presence of methyl chloride solvent. Second, aqueous and organic solutions are brought into contact, which forms polycarbonate chains. Third, fresh polycarbonate is extracted after purification and drying.
Here, in the production process, pigments with 700 to 2500 wavelengths are added to import IR-transmitting property. However, most manufacturers use Nanoparticle Coatings, Narrowband Dielectric Coatings, Multi-Layer AR Coatings, etc., to ensure the passage of infrared rays while blocking UV and visible lights.
Applications of Infrared Transmitting Polycarbonate
Infrared-transmitting polycarbonate is used in numerous applications, which are mentioned below.
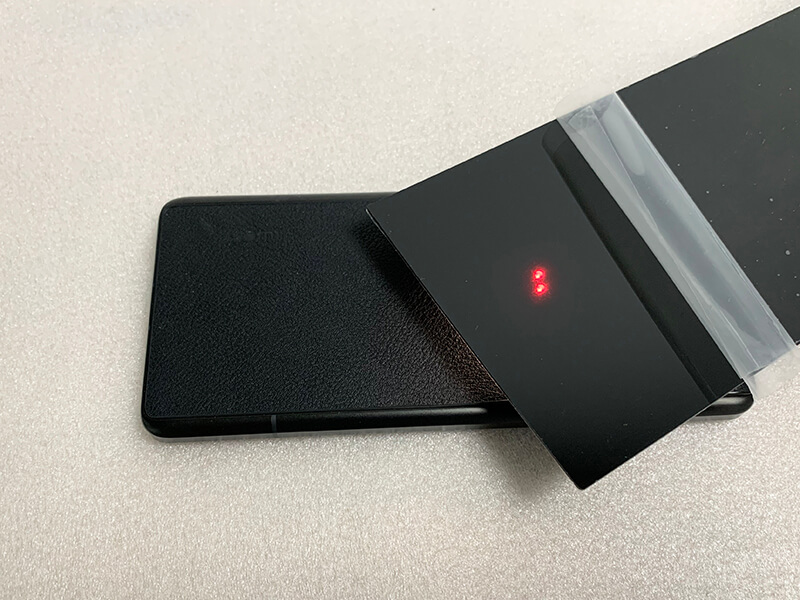
Most Common Uses
Critical Applications
Pros and Cons of Using IR Transmitting Polycarbonate
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Good IR transmission | A bit costly |
| Higher impact resistance than IR Transmitting PMMA Sheet | Can host scratch |
| Enhanced weather resistance | Limited or zero color options |
| Versatility | Heat buildup in the case of absorption |
Conclusion
Finally, we hope that you have understood the wide variety of uses of infrared transmitting polycarbonate. The diversity of its use makes us understand the importance of this construction material in various industries.
However, typically, you will be able to purchase 0.8 mm to 3 mm IR-transmitting polycarbonate with varying degrees of infrared ray transmission. The price also varies depending on many factors like manufacturing country, international tariff, thickness, size, seller type, and so on.
UVPLASTIC is a leading supplier of IR transmitting polycarbonate in China. In the meantime, it provides machining services. Contact UVPLASTIC for more information today.
Need A Trustworthy Supplier Of IRT Polycarbonate
Click on the button, you will find the Trustworthy Supplier Of IRT Polycarbonate Shee and Machining services.