What is CNC Prototyping?
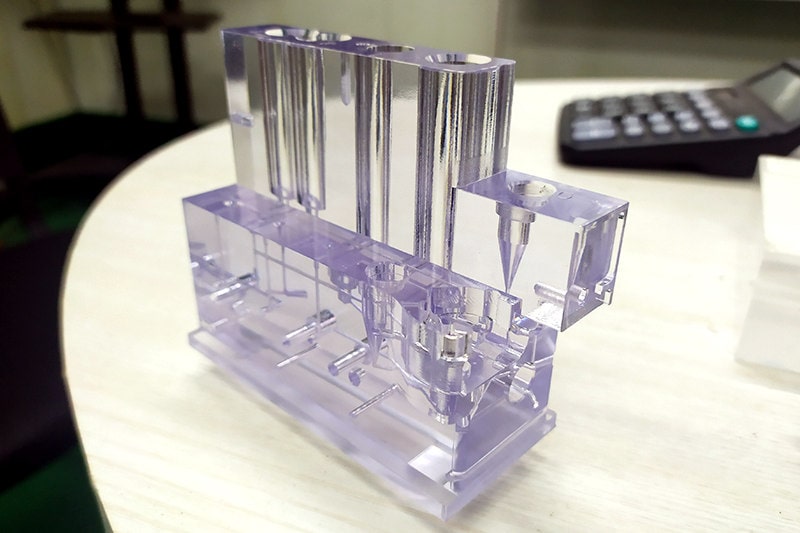
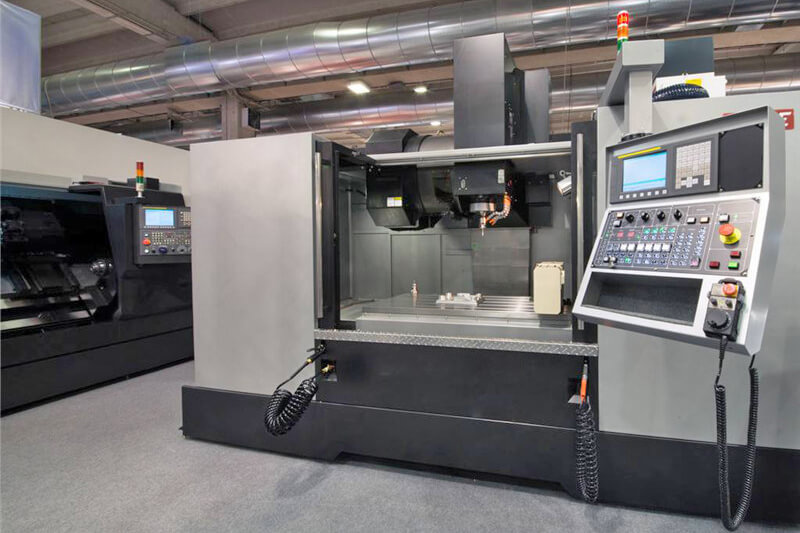
CNC prototyping (Computer Numerical Control) is a standard method of subtractive manufacturing used to build prototypes. This method uses a big chunk of solid metal known as blank and carves away from the material to get the desired shape of a prototype. Then, it uses a spinning drill to cut the materials. MIT introduced this technology in the 1950s and since then, it has been widely used throughout the manufacturing industries.
CNC works on pre-programmed numerical data, which is regulated by CAD software. This process doesn’t require any human involvement. This method is famous for manufacturing medium to high-volume products that need preciseness, durability, and greater heat resistance. CNC offers excellent iteration, a smooth surface finish, and tighter tolerance in a prototype.
.
What is 3D printing?
3D printing is quite the opposite of CNC machining. It is a popular method of the additive manufacturing process that uses thermoplastic filaments. However, 3D printing also uses CAD software like CNC to construct a prototype. In addition, photogrammetry software is also used to build a 3D object by exploring photographs. This process works by creating one layer by layer using materials like PLA, Nylon, and resins and adding those layers over one another.
This prototyping is relatively faster and cheaper compared to other techniques. This method often requires post-procession after completing the model because intersecting faces and holes are the standard error of this process. This process doesn’t need special tools or features to complete the task. A laser or heated extruder is used to solidify the layers and create the final product.
CNC machining vs 3D Printing: What’s the Difference?
CNC machining and 3D printing are the two most recognized manufacturing methods used for constructing prototypes. Both of the methods use the opposite process to achieve the result. Both ways have an advantage over one another, depending on the field. Other vital factors differentiate these two processes from each other. Let’s get a look into them.
Material Option
Both CNC machining and 3D printing are flexible in terms of material selection. These processes offer a wide range of materials for selection by manufacturers. 3D Printing primarily focuses on plastics to build a prototype, while CNC offers plastic and solid metal blocks. But, as technology is evolving every day, manufacturers have developed 3D printing metals such as 3D Systems, Arcam, Desktop Metal, and Markforged.
The most commonly used metal in CNC machining is aluminum due to its recyclable features and protective qualities. It can create high-quality prototypes for machining. Magnesium alloy, Zinc alloy, and stainless steels are other metals used in this process. CNC also includes plastics like Nylon, polycarbonate, PEEK, PP, and Acrylic to create prototypes.
On the other hand, 3D printing commonly uses thermoplastics like PLA, ABS, and ULTEM. The most common metal used for 3D Printing is stainless steel, Aluminum, Inconel, and titanium. Niche 3D printers allow the construction of prototype parts with ceramics, sand, and even living materials. But constructing a metal prototype using 3D Printing is very expensive; high-end machines are required. Furthermore, flexible materials like superalloys or TPU can’t be created with CNC machining, so 3D Printing is the only option.
Dimensional Accuracy
When it comes to tolerance, CNC machining is better compared to other 3D printing (+/-0.025 – +/-0.125 tolerance mm). CNC machining offers tight tolerance and great iteration. In 3D printing, the tolerance rate depends on the machine, material, and part geometry. Industrial machines can construct parts with an excellent dimensional tolerance of +/- 0.005 and a compliant surface for press-fitting. Tight tolerance can be post-machined in a 3D-printed product.
CNC machining can accurately create parts of any size with a smooth surface finish. However, SLS and DMLS (Powder bed fusion 3D Printing process) are incompatible with making larger volumes.
However, 3D Printing is ideal for constructing parts that have complex geometry as they have less geometric restriction compared to CNC machining. Some geometries are impossible with CNC machining even after using a 5-axis CNC system as the tools can’t enter all the parts of the component’s surface. SLS and Jet fusion can create prototypes with higher complex geometry without any support structure.
Cost and Time
Cost varies depending on the volume of the product you want to construct. For low-volume production, 3D printing is more appropriate. CNC machining is suitable for large-scale production. But if you want a quick delivery of a product, we recommend you follow the 3D printing process. CNC Machining requires specialists to operate the machines and the maintenance costs of those, making it more expensive. However, the materials and consumables are cheaper in CNC compared to 3D Printing. If you have more than 10-20 units to produce, CNC machining is more advantageous, but 3D printing is more efficient for less than that.
Waste
As we stated earlier, CNC machining includes carving away materials from an original block, which produces a lot of waste. Meanwhile, 3D printing in most instances uses the exact amount of material needed to manufacture, resulting in less waste production than CNC machining.
Let’s not forget that 3D printing doesn’t need any support structure to manufacture a prototype, so you won’t need extra materials to create those things.
Post-processing Methods
Rapid prototyping offers various post-processing methods to improve the aesthetics and give a better look to the final product.
In the CNC machining process, Bead blasting, anodizing, and powder coating are well-known methods of post-procession. At the same time, 3D printing uses techniques such as Media blasting, sanding and polishing, micro-polishing, and metal plating.
Rule of Thumb
It is essential to select the proper technique for your product development, including your hard work, money, and time. Let us help you choose which method is perfect for you by following the rule of thumb.
Final words
There is no clear winner between these two methods. Both of the methods are relatively cost-efficient and effective in their way. If you ask which one is the best? It depends on the production scale, material, geometrical complication, and budget. Though CNC machining is widely used across industries for mass production, 3D printing has increased significantly in the past few years.
We hope the article above gave you a firm idea of the differences between methods and will help you select the perfect one for you.
UVPLASTIC is a professional supplier of CNC machining services and 3D printing in China, if you are looking for a supplier, contact them now!